Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
The gastrointestinal system
Anatomy of the gastrointestinal system
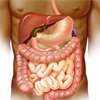 | The gastrointestinal tract (GIT) consists of a hollow muscular tube starting from the oral cavity, where food enters the mouth, continuing through the pharynx, oesophagus, stomach and intestines to the rectum and anus, where food is expelled. |
For more information, see Gastrointestinal System.
Types of inflammatory bowel disease
Overview of inflammatory bowel disease
 | Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) refers to a group of conditions characterised by recurring inflammation of the gastrointestinal organs. The two main types of IBD are ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. These are caused by immune system dysfunction. There are also a few other conditions that fall under the banner of IBD, but which do not involve immune system dysfunction. |
For more information, see Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Overview.
Crohn’s disease
 | Crohn’s disease is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory disorder that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus, as well as other organs of the body. The main pathological features of Crohn’s disease are ulcers, connection of the bowel lumen with surrounding structures (fistulae) and scar tissue leading to narrowing of the bowel lumen. |
For more information, see Crohn’s Disease.
Ulcerative colitis
 | Ulcerative colitis is a chronic systemic inflammatory disorder. Gastro-intestinal involvement is limited to the large intestine compared with Crohn’s Disease which can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract. Ulcerative colitis usually causes inflammation of the rectum and then extends further-up to involve various degrees of the colon. Sometimes it is limited to just a small section of the left-hand side of the colon. |
For more information, see Ulcerative Colitis.
Video: Dr Joe Kosterich explains ulcerative colitis
 | There are a number of causes of abdominal illnesses, and one of the ones that is quite serious – treatable, but less common – is ulcerative colitis. Dr Joe Kosterich talks about ulcerative colitis, including what it is, what its symptoms are, how it is diagnosed and how it is treated. |
Watch the video Ulcerative Colitis.
Video: Dr Andrew Day talks about Crohn’s and colitis in children
 | In children Crohn’s disease can lead to malnutrition, iron-deficiency anaemia, growth retardation and even delays in puberty. Dietary therapy is particularly important in the management of this disease in children. Steroid treatments may be used but they can have serious side effects on growth and bone mineral density (occasionally leading to osteoporosis). |
Watch the video Crohn’s and Colitis in Children.
Investigations
Colonoscopy
For more information, see Colonoscopy.
Supportive Care
Crohn’s & Colitis Australia
 | As Australia’s peak patient body representing people with inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s and Colitis Australia is a non-profit organisation “committed to finding a cure while providing support for the care and wellbeing of people living with crohn’s disease and colitis”. They focus on education, advocacy, counseling, increasing awareness and generating and utilising funds for research and support. |
For more information, see Crohn’s & Colitis Australia.
Dates
Tags
Created by:

 Login
Login