Lipitor
Generic Name: Atorvastatin calcium
Product Name: Lipitor
Indication
Lipitor is used for treating hypercholesterolaemia, that is, high levels of blood cholesterol. It should only be used by individuals who are concurrently treating their high cholesterol levels with dietary modifications. A doctor will check that secondary causes of high cholesterol (e.g. poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, hypertension, alcoholism) have been identified and treated before prescribing Lipitor.
Lipitor is also sometimes used to prevent non-fatal heart attack and stroke in individuals with hypertension and other risk factors for coronary heart disease. However, it will only be prescribed for heart attack and stroke prevention in individuals who are also taking other measures to control these conditions, such as controlling diabetes and/or hypertension, and quitting smoking.
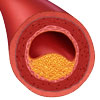 | For more information on cholesterol, including the health effects of high cholesterol and ways to lower cholesterol levels, as well as some useful tools, see Cholesterol. |
Action
The active ingredient in Lipitor, atorvastatin, works to lower lipid levels by inhibiting the production of cholesterol in the liver. It also reduces the activity of low-density lipoproteins (LDL cholesterol) in the liver. LDLs are the lipoproteins that transport cholesterol through the blood to the body’s cells. By reducing the activity of LDL, the amount of cholesterol transported into the body’s cells is also reduced.
Dose advice
Dose information
Lipitor is taken once a day and can be taken with or without meals. Most individuals will use the medication to treat primary hypercholesterolaemia or dyslipidaemia, and these people will start by taking a single 10 mg Lipitor tablet every day. Treatment with Lipitor aims to reduce lipid levels to an appropriate level, so the dose may be adjusted depending on the degree to which lipid levels change with the 10 mg daily dose. A doctor will assess lipid levels after four weeks of therapy and adjust the dose accordingly.
For individuals receiving treatment for homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia, the recommended dose is 80 mg daily.
Contraindications
Lipitor should not be used by individuals who:
- Are allergic to any component of the medication;
- Have liver disease;
- Have elevated blood transaminase levels;
- Are women of reproductive age and not using adequate contraceptive protection.
Precautions
Because there is an increased risk of side effects or complications in some groups of people, doctors will be cautious about prescribing Lipitor to some individuals, including those:
- With liver dysfunction or a history of liver disease: Lipitor is known to affect liver functioning. The doctor will usually perform a liver function test in these individuals before prescribing Lipitor, and regular liver function tests throughout Lipitor therapy. Individuals who experience reduced liver function whilst taking Lipitor may have their dose reduced, or the treatment may be stopped;
- Taking other medications which may affect the action of Lipitor or increase the risk of side effects. These drugs include cyclosporin, macrolide antibiotics, azole antifungals, efavirenz, rifampicin, phenytoin, antacids, colestipol, transport inhibitors, protease inhibitors, diltiazem hydrochloride, intraconazole and grapefruit juice;
- Who consume alcohol in substantial quantities;
- Who have recently experienced stroke. Lipitor treatment has been shown to increase the risk of stroke.
A number of conditions indicate an increased risk to health from Lipitor therapy. Therapy is usually withdrawn if any of the following conditions occur:
- Muscle disorders;
- Increased creatine kinase levels;
- Interstitial lung disease;
- Risk factors for acute renal failure caused by rhabdomyolysis. These include:
- Hypotension; and
- Metabolic, hormone and electrolyte disorders.
Lipitor is also known to affect the action of digoxin and oral contraceptives.
Use in pregnancy
Lipitor is a Category D medication. It should not be used by pregnant women as it appears to cause foetal malformation.
Use in breastfeeding
Lipitor should not be used in breastfeeding as there is insufficient evidence regarding its safety.
Schedule
Lipitor is a Schedule 4 medication.1
Common side effects
All medications produce side effects in some of the people who use them. While these are usually minor complications, they can sometimes be serious. The doctor will assess the risk of an individual developing side effects before prescribing the medication.
Lipitor is usually well tolerated, and the side effects that occur are usually mild and temporary.
Common side effects are those which occur in more than 1% of people given Lipitor. These include:
- Headache;
- Asthenia (lack of energy);
- Abdominal pain;
- Indigestion;
- Nausea;
- Flatulence;
- Constipation;
- Diarrhoea;
- Insomnia;
- Myalgia (muscle pain).
Uncommon side effects
Side effects that occur in less than 1% of people given Lipitor are considered uncommon. People do not necessarily experience any of these side effects, so do not become alarmed by this list:
- Vomiting;
- Appetite/weight loss;
- Jaundice;
- Muscle cramps;
- Muscle inflammation;
- Itching;
- Deafness;
- Hypoglycaemia;
- Hyperglycaemia;
- Haemorrhagic stroke.
Rare side effects of Lipitor are those that occure in less than 0.1% of users. These include:
- Hepatitis;
- Pancreatitis;
- Hair loss;
- Paraesthesia (pins and needles);
- Peripheral neuropathy;
- Impotence;
- Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis;
- Chest pain;
- Malaise;
- Fatigue;
- Rhabdomyolysis;
- Hypoaesthesia (loss of skin sensitivity to touch or pain);
- Dizziness;
- Amnesia;
- Dysgeusia (abnormal taste);
- Tinnitus;
- Rashes;
- Urticaria;
- Peripheral oedema;
- Weight gain;
- Thrombocytopaenia;
- Tendon rupture;
- Gynaecomastia;
- Interstitial lung disease.
If you experience any of the listed side effects, or any other symptoms which appear abnormal or unusual, please tell your doctor.
References
- Product Information: Lipitor. West Ryde, NSW: Pfizer Australia; 11 August 2010.
- Atorvastatin [online]. Adelaide, SA: Australian Medicines Handbook; July 2009 [cited 2 December 2009]. Available from: [URL link]
Diseases treated by Lipitor:
Treatments associated with Lipitor:
For further information talk to your doctor.
Dates
Created by:

 Login
Login













